Physical therapy, Electromagnetic field
Galvanotherapy
What is galvanotherapy?
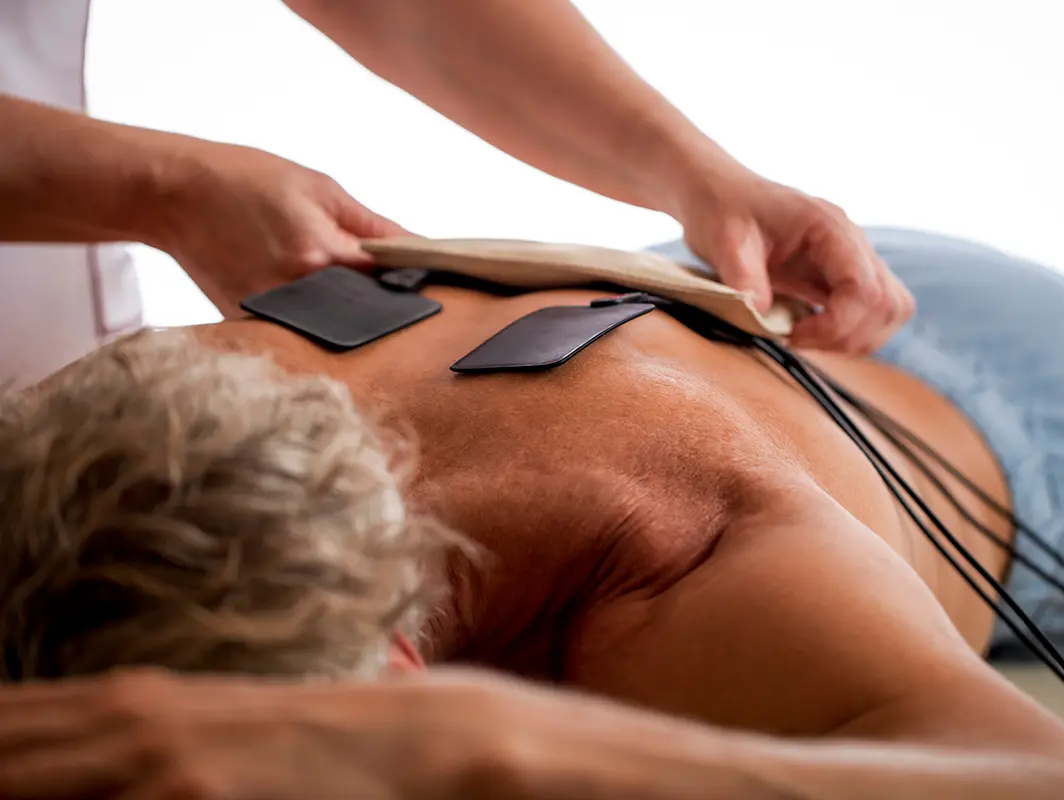
Galvanic current is a direct current that changes the electrical charge of the tissues and thus affects the activity of the capillaries to the best appropriate tissue perfusion. The most common method of application is by means of electrodes positioned on the body with wet protective sheaths. The size and location of the neutral electrodes as well as their polarity are prescribed by the doctor because they substantially affect the healing result. The treatment takes at least half an hour to produce the necessary effect. Other possible applications are those in the form of a full body bath or a partial galvanic bath.
Benefits of electroplating
Positive cations irritate adjacent tissues and improve tone, improving blood perfusion. Such an effect is beneficial in peripheral circulatory disorders (eg Raynaud's syndrome, post-traumatic swelling). Negative anions reduce electrical irritation and suppress painful or otherwise unpleasant sensations (for example, in neuropathies). The direct current does not produce muscle contraction, but you may feel tingling (which later disappears) and you may notice a redness of the affected area. These are beneficial effects.