Physical therapy, Electromagnetic field
Electrotherapy
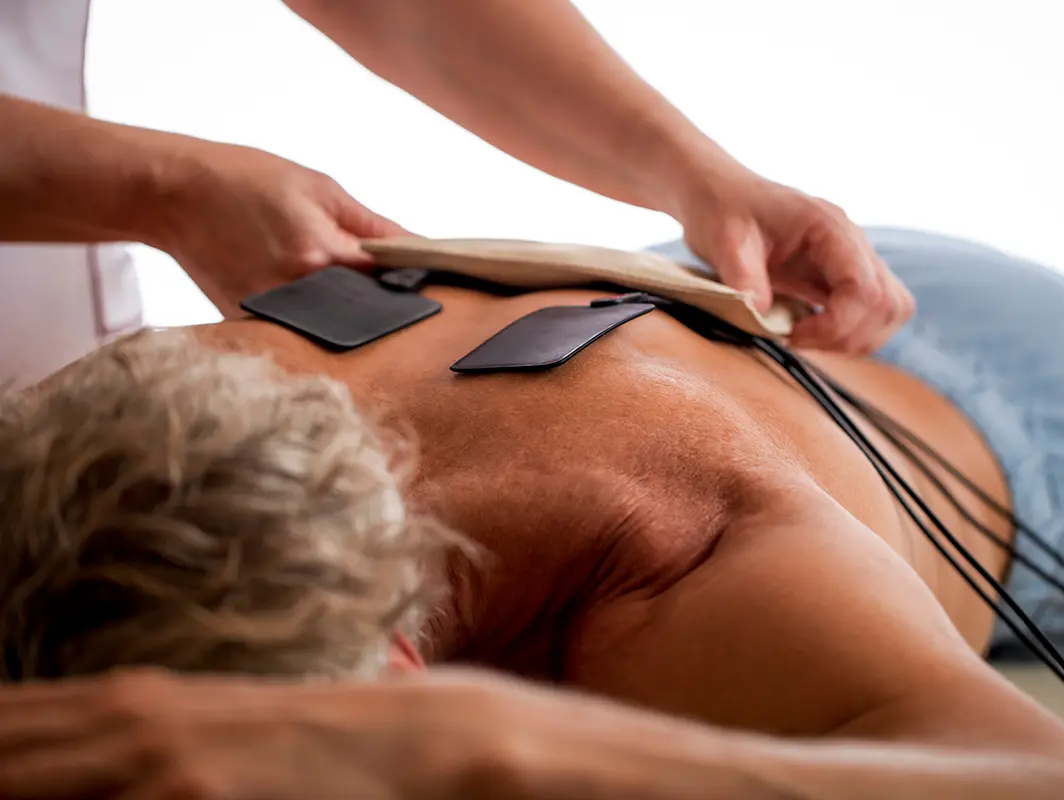
What is electrotherapy
Because the human body contains an average of 60% water, it is basically a very good conductor of electricity. Electrotherapy uses different types of electric currents to influence the function of electroconductive tissues in the human body. Nerves and muscles are best treated with electricity. Connective tissues can also be affected by electrotherapy. Some currents that penetrate deep into the body can positively affect the functions of certain internal organs (such as the bladder or large intestine). Currents used for curative purposes have been carefully tested and their safety and efficacy have been demonstrated. We use direct or alternating currents (low, medium or high frequency) depending on the effect we need to achieve.
Benefits of electrotherapy Electric
currents cause changes in the electrical characteristics of affected tissues, causing various healing effects: suppression of pain, relaxation or stimulation of muscles, relaxation of rigid tissues, improved blood circulation, reduced swelling, improved immunity, improved inflammation. The precision effect of electrotherapy depends on the quality of the current - modulation of frequency or amplitude, its intensity, etc.